复合模式,也称为部分整体模式,用于将一组相似的对象视为单个对象。组合模式根据树状结构组合对象,用于表示部分和整体级别。这种类型的设计模式属于结构模式,它创建了对象组的树形结构。
意图
将对象组合成树形结构,以表示“部分-整体”层次结构。组合模式使用户能够以一致的方式使用单个对象和组合对象。
解决问题
在我们的树结构问题中,它模糊了简单元素和复杂元素的概念,客户端程序可以像处理简单元素一样处理复杂元素,从而将客户端程序的内部结构与复杂元素解耦。
UML图
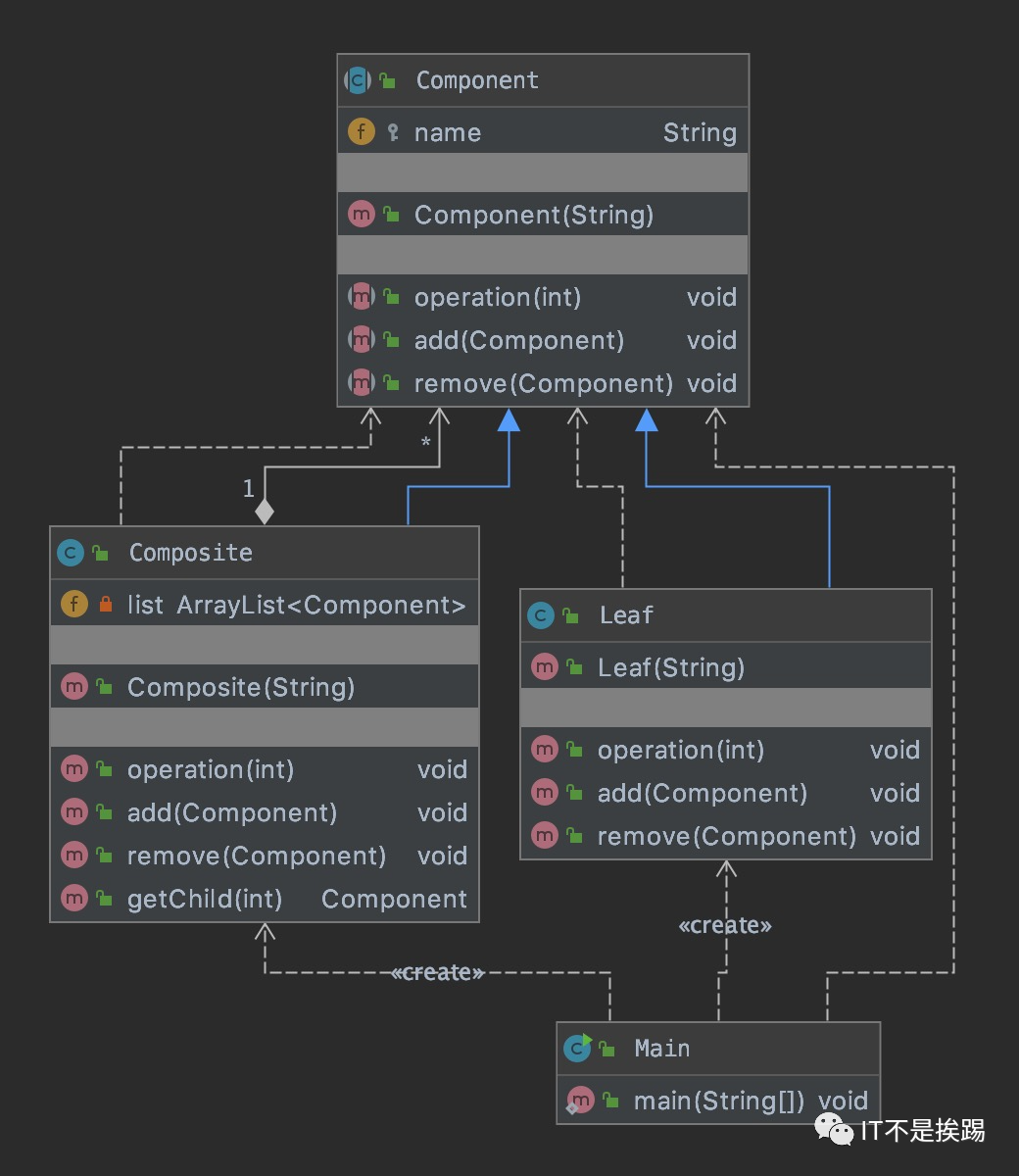
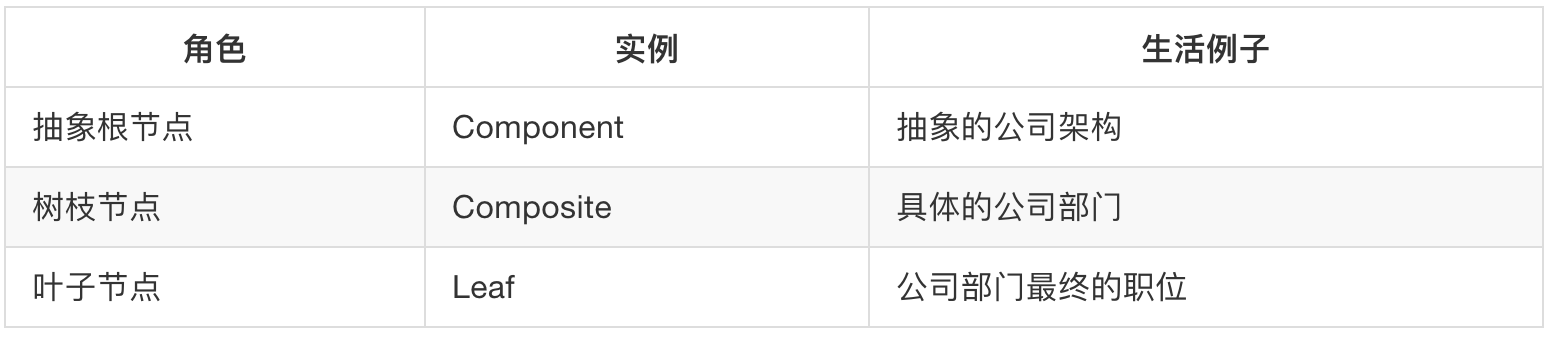
该模式包含的角色及其职责
抽象根节点(Component)
定义系统各级对象的常用方法和属性,可以提前定义一些默认行为和属性。
树枝节点(Composite)
定义分支节点的行为,存储子节点,将分支节点和叶节点组合形成树形结构。
叶子节点(Leaf)
叶对象,下面没有分支,是系统层次遍历的最小单元。
在这个例子中:
优缺点
优点
复杂的对象是分层表示的,很容易添加新的节点。
客户端调用很简单,客户端可以一致地使用复合结构或其中的单个对象。
在程序集中添加对象组件更容易,客户端不必因为添加新的对象组件而更改原始代码。
缺点
当使用复合模式时,它的叶子和分支的声明都是实现类,而不是接口,这违反了依赖反转的原则。
让设计更加抽象。如果对象的业务规则非常复杂,那么实现复合模式是非常具有挑战性的,而且并不是所有的方法都与叶对象的子类相关。
应用场景
当你想表达对象的部分-整体层次结构时,比如公司的父子关系、分销体系、产品品牌分类。
当您希望用户忽略组合对象和单个对象之间的差异时,用户将统一使用组合结构中的所有对象。
案例背景
例如,公司的组成通常由多个部门组成。现在我们有一个公司,有多个部门,部门里有很多职位。让我们来看看这种组合模式。
组织架构
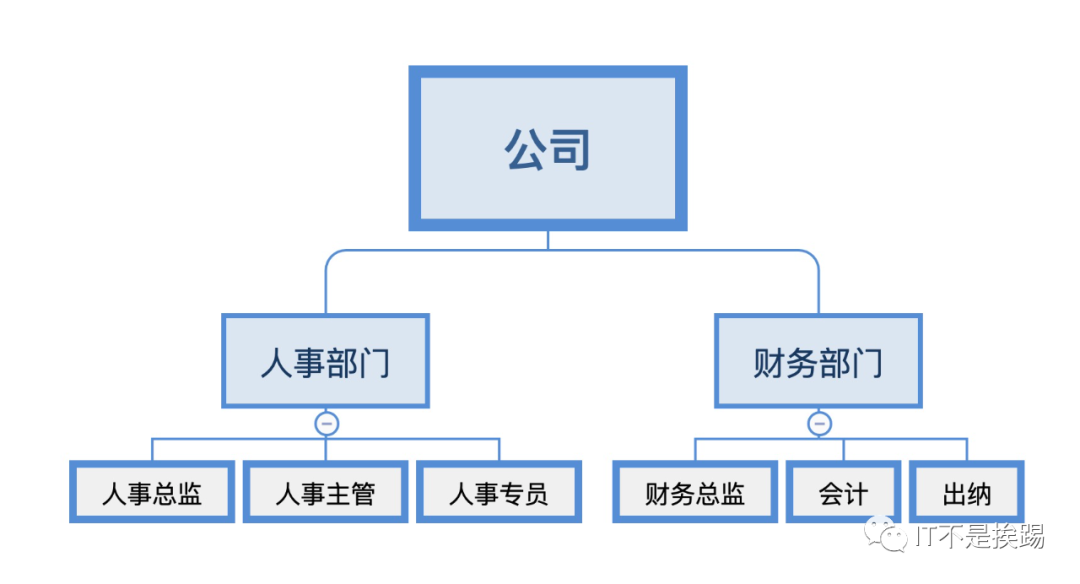
用代码把上面的图片转换成下面的形式。

应用场景
php的抽象公司结构(组件)
抽象类组件
{
受保护的$ name
/**
*组件构造函数。
* @param $name
*/
公共函数_ _ construct($ name){ 0
$ this-name=$ name;
}
公共抽象函数操作($ depth);
公共抽象函数add(Component $ Component);
公共摘要f
unction remove(Component $component); }Composite.php 具体的公司部门(Composite)
class Composite extends Component
{
private $componentList;
public function operation($depth){
echo str_repeat('-', $depth) . $this->name . PHP_EOL;
foreach ($this->componentList as $component) {
$component->operation($depth + 2);
}
}
public function add(Component $component){
$this->componentList[] = $component;
}
public function remove(Component $component){
$position = 0;
foreach ($this->componentList as $child) {
++$position;
if ($child == $component) {
array_slice($this->componentList, $position, 1);
}
}
}
public function getChild(int $i){
return $this->componentList[$i];
}
}Leaf.php 公司部门最终的职位(Leaf)
class Leaf extends Component
{
public function operation($depth){
echo str_repeat('-', $depth) . $this->name . PHP_EOL;
}
public function add(Component $component){
echo "Cannot add to a leaf".PHP_EOL;
}
public function remove(Component $component){
echo "Cannot remove from a leaf".PHP_EOL;
}
}调用代码:
$root = new Composite("公司");
// 添加人事部门
$rs = new Composite("人事部门");
// 添加人事部门下面的职位
$rs->add(new Leaf("人事总监"));
$rs->add(new Leaf("人事主管"));
$rs->add(new Leaf("人事专员"));
$root->add($rs);
// 添加财务部门
$cw = new Composite("财务部门");
// 添加部门下面的职位
$cw->add(new Leaf("财务总监"));
$cw->add(new Leaf("会计"));
$cw->add(new Leaf("出纳"));
$root->add($cw);
$root->operation(0);
$child = $root->getChild(0);
print_r($child);输出结果:
公司
--人事部门
----人事总监
----人事主管
----人事专员
--财务部门
----财务总监
----会计
----出纳
// 通过 getChild 获取的某个部门对象
Composite Object
(
[Composite:private] => Array
(
[0] => Leaf Object
(
[name:protected] => 人事总监
)
[1] => Leaf Object
(
[name:protected] => 人事主管
)
[2] => Leaf Object
(
[name:protected] => 人事专员
)
)
[name:protected] => 人事部门
)如果觉得文章还不错,请把文章分享给更多的人学习,在文章中发现有误的地方也希望各位指出更正。现有误的地方也希望各位指出更正。

 2021-11-07 16:59:15
2021-11-07 16:59:15